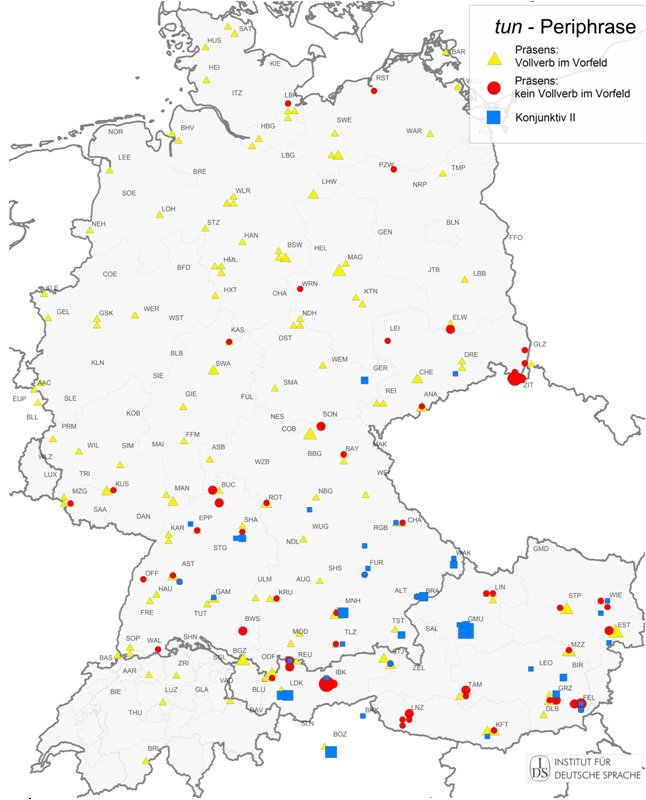
Die tun-Periphrase
Functions of do-periphrasis in English
There are three functions of do-periphrasis in English:
- the formation of negation sentences (I did not answer the question.),
- the formation of interrogatives (Did you answer the question?), and
- the formation of focus readings (I did answer the question.).
tun als Vollverb / tun as a full verb in German
Obwohl viele Menschen der Meinung sind, man sollte tun nicht verwenden, wird es ganz normal als Vollverb verwendet.
Although many people think you should not use tun, it is frequently used as a full verb in German.
Although many people think you should not use tun, it is frequently used as a full verb in German.
Er hat viel für uns getan. / He has done a lot for us.
Mein Bein tut weh. / My leg hurts.
Mein Bein tut weh. / My leg hurts.
tun als Hilfsverb ("periphrastische" Verwendung) / tun as an auxiliary verb (periphrastic usage)
1. Mit Vollverb im Vorfeld / With full verb in the prefield
The Full verb in infinitive is followed by finite auxiliary tun. The full verb is emphasized by its position in prefield ("verb topicalization"). This use of tun is considered correct and standard language by grammars.
2. Vollverb nicht im Vorfeld: tun im Indikativ / Full verb not in prefield: tun in indicative
The full verb is not in prefield, but forms the right sentence bracket. This construction is evaluated as "colloquial" in normative grammars.
3. Vollverb nicht im Vorfeld: tun im Konjunktiv II / Full verb not in prefield: tun in subjunctive II
This construction is often classified as a "vernacular", i.e. regionally limited expression of the subjunctive mood.
Lügen tut man nicht! / One does not lie!
Wirklich mögen tut er sie nicht. / He does not really like her.
Das Vollverb im Infinitiv wird gefolgt vom finiten Hilfsverb tun. Das Vollverb wird durch die Stellung im Vorfeld betont ("Verb-Topikalisierung"). Dieser Gebrauch von tun wird von Grammatiken als korrekt und standardsprachlich angesehen.
Wirklich mögen tut er sie nicht. / He does not really like her.
The Full verb in infinitive is followed by finite auxiliary tun. The full verb is emphasized by its position in prefield ("verb topicalization"). This use of tun is considered correct and standard language by grammars.
2. Vollverb nicht im Vorfeld: tun im Indikativ / Full verb not in prefield: tun in indicative
Manche lesen gerne, ich tue lieber Musik hören. / Some like reading, I prefer reading.
Er tut immer die Tür offenlassen. / He always leaves the door open.
Hier steht das Vollverb im Infinitiv nicht im Vorfeld, sondern bildet die rechte Satzklammer. Diese Konstruktion wird in normativen Grammatiken als "umgangssprachlich" bewertet.
Er tut immer die Tür offenlassen. / He always leaves the door open.
The full verb is not in prefield, but forms the right sentence bracket. This construction is evaluated as "colloquial" in normative grammars.
3. Vollverb nicht im Vorfeld: tun im Konjunktiv II / Full verb not in prefield: tun in subjunctive II
Es täte ihm nicht gefallen, wenn sein Sohn eine schlechte Note bekommmt. / He would not like it if his son got a bad grade.
Ich täte mich sehr freuen, wenn du kommst. / I would be very happy, if you came.
Diese Konstruktion wird häufig als "landschaftlicher", d.h. regional begrenzter Ausdruck des Konjunktivs eingeordnet.
Ich täte mich sehr freuen, wenn du kommst. / I would be very happy, if you came.
This construction is often classified as a "vernacular", i.e. regionally limited expression of the subjunctive mood.
Regionale Variation in der Benutzung / Regional variation in usage